Air Source Heat Pumps Explained
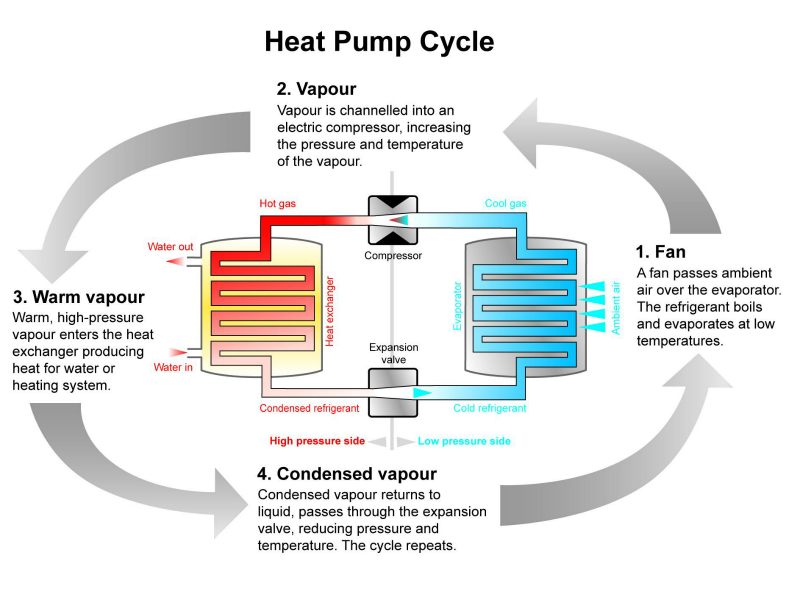
Air source heat pumps (ASHP) is a process that by using the principle of vapour compression, transfers the hot air from a place to another exactly in the same way as the system of a refrigerator does.
Before looking at the details of the technology, it is important to note that air at a temperature above absolute zero always contains some heat and many of these heat pumps manage to extract heat even at low temperatures as -15 C degrees.
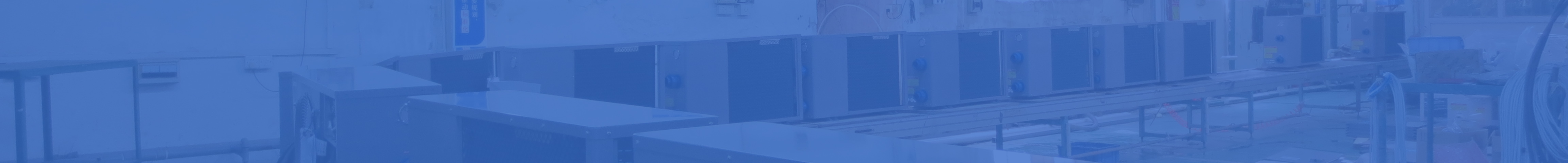
Air source heat pumps systems consist of four major elements that allow the refrigerant to pass from the liquid state to the gas:
1.A compressor
2.A condenser
3.An expansion valve
4.An evaporator
When the refrigerant passes through the heating system, the high temperature (usually 100 degrees or more) transforms it into vapour or gas while the energy produces heat.
The gas then goes through the compressor that increases its temperature, and then through the expansion valve that makes the hot air enter the building.
Next, the hot air passes in a condenser that turns the gas into liquid again. The heat produced by the energy in the evaporation phase passes through the heat exchanger again to restart the cycle and it is used to make the radiators work, for underfloor heating (air-to-air system) or for domestic hot water (air-to-water heat pump system).
Measures of Efficiency and Benefits of Air Source Heat Pumps
Air source heat pumps performances are measured through a Coefficient of Performance (COP) that can have different values that mean how many units of heat are produced using one unit of energy.
There are many advantages of air source heat pumps, both on environmental and economic sides.
First of all, air source heat pumps don’t have an environmental impact as significant as the heat they use for the process is extracted either by air, water or ground and it is continuously regenerated although they still make use of electricity in the process.
On the financial side, air source heat pump cost can be reduced with the help of the State through the Renewable Heat Incentive, and householders can reduce carbon emissions by cutting on harmful fuels.
Furthermore, this technology does not need frequent maintenance but it usually works smoothly after the installation and it is cheaper to install than ground source pumps as it does not need any kind of excavation site.
However, it could be less efficient than the ground pump and its performance can be negatively affected by low temperatures and it usually needs a longer time and bigger surfaces to heat the interiors.
Post time: Mar-16-2022

